In today’s world, many industries require round-the-clock operations to meet consumer demands and maintain critical services. From healthcare to manufacturing, organizations rely on shift work to ensure continuous productivity. One popular approach is the 12-hour rotating shift. Essentially, it’s a work schedule designed to provide 24/7 coverage while balancing employee well-being with operational demands.
If you’re new to the concept or wondering whether this might be the right fit for your organization, let’s explore what a 12-hour rotating shift entails. We’ll also look at how it works, the industries that use them, and the potential benefits and challenges involved.
What is a 12-Hour Rotating Shift?
A 12-hour rotating shift is a structured schedule where employees alternate between day and night 12-hour shifts over a set period. This usually includes a mix of workdays and days off. This schedule gives employees regular breaks while keeping staffing steady.
For example, in a rotating employee schedule, an employee may work several 12 hour day shifts in a row. After that, they have a few days off before switching to 12-hour night shifts. This rotation helps balance workload, prevents employee burnout, and provides staff with the chance to recharge during off days.
Why Do Organizations Use 12-Hour Rotating Shifts?
Many organizations use 12-hour shift schedules and rotating shifts. This helps them operate 24/7 without overworking employees. This scheduling model is particularly valuable in sectors where continuous coverage is essential for productivity or safety.
By implementing a rotating schedule, companies can maintain efficient operations while allowing employees sufficient time off. The 12-hour rotating model is different from the usual eight-hour shifts over five days. It gives shift workers consecutive days off. This change helps improve their work-life balance.
Common Industries Using 12-Hour Rotating Shifts
Numerous industries benefit from this shift model, particularly those that require uninterrupted services or production lines. Here are a few examples:
• Healthcare: Hospitals and emergency services depend on rotating shifts to ensure that patient care remains available around the clock. A twelve hour shift rotation allows for sufficient staffing while providing healthcare workers with the necessary recovery time.
• Manufacturing: Continuous production is crucial in sectors like automotive, food, and pharmaceuticals. A rotating shift enables companies to meet production demands without compromising the health and safety of their workforce.
• Emergency Services: Police departments, fire services, and ambulance providers rely on shift rotations to maintain immediate response capabilities. This model ensures that personnel are readily available at any hour, improving response times and overall community safety.
• Energy and Utilities: Power plants, oil refineries, and utility companies operate 24/7 to meet public and industrial demands. A 12-hour rotating schedule allows these facilities to maintain steady output without exhausting employees.
Common 12-Hour Rotating Shift Patterns
Various rotation patterns help companies achieve balanced schedules while meeting operational goals. Here are some of the most commonly used:
DuPont Schedule:
This 28-day cycle has teams working four night shifts in a row. They then get three days off. After that, they work three day shifts and take one day off.
Next, they work three night shifts and have three days off again. Finally, they work four day shifts before enjoying a full week off each month.
2-3-2 (Pitman) Schedule:
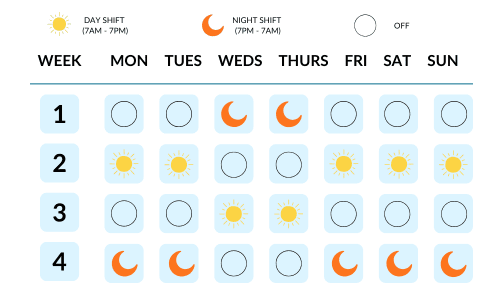
In a two-week cycle, employees work two day shifts. Then, they have two days off. Next, they work three day shifts. After that, they take another two days off. They work two more day shifts.
Finally, they enjoy a long weekend with three days off. This schedule rotates between day and night shifts, providing every other weekend off.
4 On, 4 Off Schedule:
Employees work four consecutive 12-hour shifts (either day or night), followed by four days off. This schedule provides predictable extended rest periods and can be easier to manage from a work-life balance perspective.
Advantages of 12-Hour Rotating Shifts
Using a 12-hour rotating shift model brings several benefits to both employees and employers.
• Enhanced Coverage: By scheduling employees on a rotation, organizations maintain continuous operations, meeting production demands or ensuring client safety and service.
• Increased Time Off: While 12-hour shifts are lengthy, this structure allows employees to enjoy longer blocks of time off compared to traditional workweeks. This extended time can reduce burnout and enhance job satisfaction.
• Less Frequent Commuting: For employees, fewer days at work mean fewer commutes. This can result in savings on travel expenses and more personal time.
Challenges of a 12-Hour Rotating Shift
Despite the benefits, rotating shifts aren’t without challenges. Organizations should consider these factors when implementing a 12-hour rotating schedule:
• Risk of Fatigue: The length of a 12-hour shift can lead to fatigue, especially if the workload is demanding. This can impact performance, safety, and even mental health if the shift worker if not managed well.
• Sleep Disruptions: Constantly switching between day and night shifts can affect an individual’s circadian rhythm, which regulates sleep. Proper sleep management and sleep schedules are essential for maintaining health and productivity in a rotating schedule.
• Balancing Work-Life Demands: Although employees have extended days off, working long shifts can make it difficult to maintain personal commitments during work periods. This can be particularly challenging for those with family or caregiving responsibilities.

Tips for Implementing 12-Hour Rotating Shifts
To maximize the benefits of a 12-hour rotating shift model while mitigating the challenges, consider these best practices:
• Involve Employees in Planning: Engaging employees during the scheduling phase can foster acceptance and address individual needs, creating a supportive work environment.
• Focus on Health and Safety: Encourage healthy habits, regular breaks, and provide resources for managing fatigue. Consider wellness programs that support sleep health and stress management.
• Ensure Compliance with Labor Laws: Rotating schedules should adhere to local labor laws, especially regarding break times, overtime, and safety requirements.
A 12-hour rotating shift is a strategic scheduling approach that supports industries needing constant operation. Balancing operational needs with employees’ work-life balance can help ensure efficiency and satisfaction.
This approach is practical and beneficial for everyone. For organizations thinking about this schedule, a careful approach is important. Listening to employee feedback and using helpful practices will lead to better results.




