In the realm of human resources, staffing, and business management, understanding various metrics can provide valuable insights. One such metric is the Full-Time Equivalent (FTE). Although it might sound like jargon, FTE is essential for businesses big and small. In this post, we’ll dive deep into the concept of FTE, explaining what it is and how to calculate it effectively.
Understanding the Basics: What is FTE?
What It Means
FTE (full time equivalent) is a measure that compares workloads of employed people in different situations. An FTE of 1.0 is equivalent to a full-time worker, while an FTE of 0.5 signals half of a full workload.
Why It’s Important
Knowing how to calculate FTE is particularly crucial for:
- Budgeting: Managers often use FTEs to estimate labor costs.
- Staffing: Understanding FTEs can help in determining the number of staff required.
- Analysis: For analyzing productivity, assessing labor trends, or making comparisons across departments or periods.
Using FTE to Improve Operations
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is not just a metric to measure the workforce equivalent but also a powerful tool that can be leveraged to enhance operations across various sectors. Properly understood and applied, FTE can provide insights that lead to efficiency, cost savings, and better productivity. Here’s how:
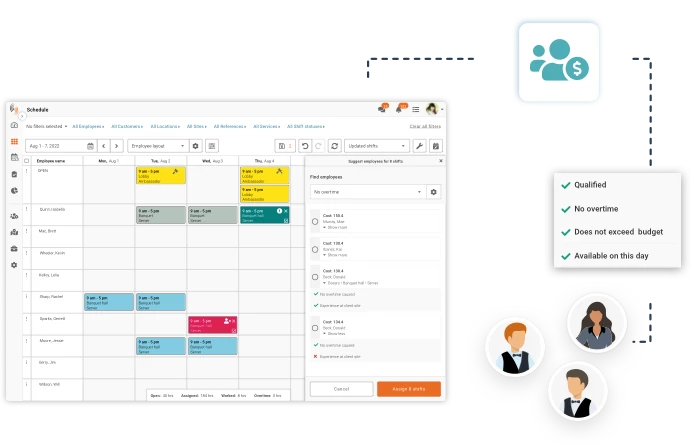
1. Resource Allocation and Planning
- Balanced Workloads: By understanding the total FTE, organizations can ensure that workloads are balanced among employees. This can reduce burnout and increase job satisfaction.
- Project Planning: For project-based operations, understanding the FTE helps in gauging how many full-time workers are required to complete a project within a stipulated time.
2. Budgeting and Financial Forecasting
- Labor Cost Predictions: Labor is often one of the most significant costs for businesses. Knowing the FTE helps businesses predict labor expenses, facilitating better financial planning.
- Expense Control: Organizations can pinpoint where they might be overstaffed and take corrective actions, either by redistributing staff or reconsidering hiring plans.
3. Enhancing Productivity
- Performance Metrics: FTE data can be used to derive metrics like revenue per FTE or units produced per FTE. These metrics can give insights into the workforce’s productivity, indicating where improvements are needed.
- Training Needs: If certain operational areas with a high FTE are underperforming, it may indicate a need for better training or resources in those areas.
4. Strategic Hiring Decisions
- Informed Recruitment: If a company has a high number of part-time workers contributing significantly to the overall FTE, it might be more efficient to hire additional full-time employees, or vice versa, based on business needs.
- Reducing Turnover: High FTE among temporary or part-time employees might indicate a need for more stable employment options, potentially reducing employee turnover and recruitment costs.
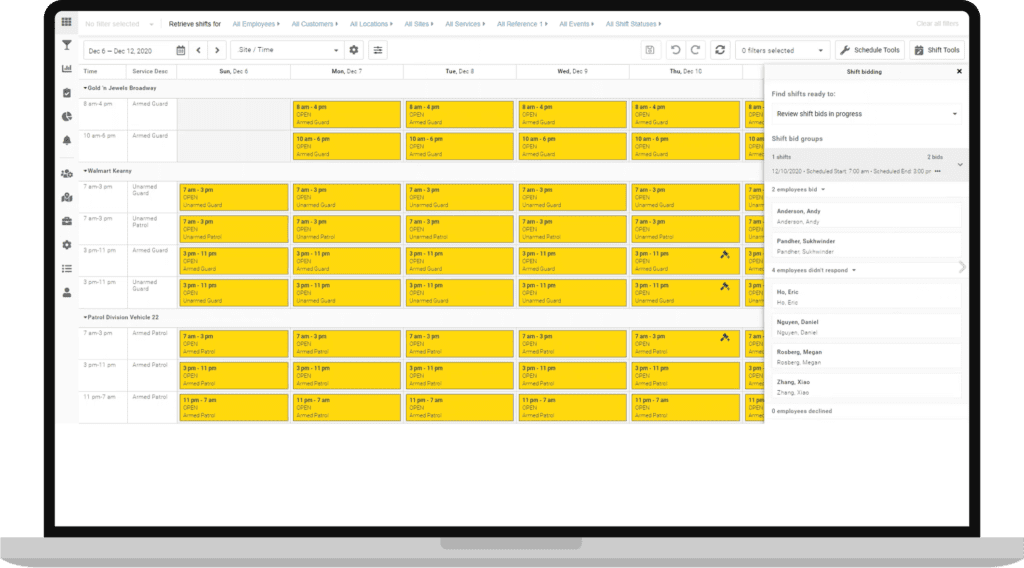
5. Shift and Schedule Optimization
- Optimal Staffing: In industries like healthcare or hospitality, understanding FTE can help managers ensure they have the right number of staff for each shift, optimizing service delivery and reducing labor costs. We’ll discuss this in more detail below.
- Flexibility: For businesses that have fluctuating demands, FTE can provide insights into creating flexible schedules, ensuring peak times are adequately staffed without overstaffing during off-peak hours.
6. Employee Morale and Satisfaction
- Employee Engagement: Recognizing areas where employees are consistently working beyond their designated FTE can be indicative of burnout or overwork. Addressing these areas can lead to higher employee satisfaction.
- Growth Opportunities: Understanding the areas with a higher FTE can also indicate where there’s potential for growth or upskilling, allowing businesses to invest in training and development.
7. Long-term Strategic Planning
- Expansion Insights: A steadily increasing FTE in certain departments can be a signal for business expansion in those areas.
- Resource Redeployment: If specific departments have a declining FTE, it may suggest that resources can be better used elsewhere or that operational strategies need rethinking.
Breaking Down the Calculation
How to calculate fte: Basic calculation
To determine FTE, simply divide the total hours worked by what’s generally considered as full-time hours. For instance, if working 40 hours a week is regarded as full-time, and an employee works 20 hours a week, then their FTE is 0.5.
How to calculate fte Considering Multiple Employees
When evaluating FTEs for a group of employees, combine the hours worked by all part-time employees and then divide by the hours typically considered as full-time. So, if you have five employees each working 20 hours weekly (combined, they work 100 hours), and full-time work is 40 hours a week, the total FTE for the group would be 2.5.
FTE in Different Contexts
In the World of Academia
In educational institutions, particularly colleges and universities, FTE often helps understand the student enrollment and teaching load. A full-time student might be considered 1 FTE, whereas two half-time students would represent the same 1 FTE.
Healthcare Sector
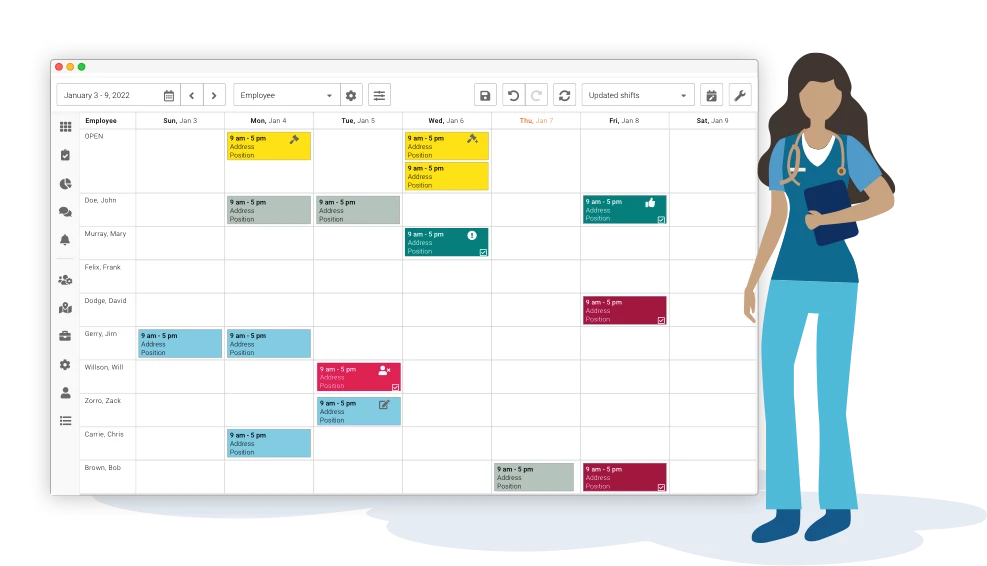
In healthcare, FTE is pivotal for budgeting and staffing. Given the unique demands of this sector in order to comply with the Affordable Care Act (aca), understanding FTE helps institutions ensure there’s always adequate staff.
Hospitality
The hospitality sector, encompassing hotels, restaurants, travel agencies, and other related services, has unique workforce dynamics. Seasonal variations, customer demands, long working hours, and part-time or casual employment arrangements are common characteristics. In such an environment, understanding Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is crucial for various operational and strategic reasons.
Tips for Calculating FTE Accurately
- Define Full-time Hours Clearly: Different businesses and sectors might have variations in what’s considered full-time. It’s vital to have a clear standard.
- Include All Worked Hours: This means considering overtime, weekends, or any extra hours put in by part-time or flexi-time workers.
- Reassess Periodically: The nature of work changes. Periodic assessment ensures that your FTE calculations remain accurate and relevant.
Misunderstandings Around FTE

FTE ≠ Headcount
It’s a common misconception that FTE and headcount are the same. Remember, FTE represents workload, not the actual number of employees. A company might have 10 employees (headcount of 10) but only an FTE of 8 if several employees are part-time.
Full-time Doesn’t Always Mean 40 Hours
Full-time hours can vary across countries, industries, or even individual companies. While 40 hours a week is standard in many places, it’s essential to be aware of local regulations or company policies.
Full-Time Equivalent (FTE) is more than just a metric; it’s a lens through which businesses can gain a clearer understanding of their workforce’s dynamics. Whether it’s for budgeting, staffing, or strategizing, a comprehensive grasp of FTE can be a game-changer for organizations. As with any metric, the key lies in understanding its nuances, applying it correctly, and using the insights derived to make informed decisions.




