This eBook is also available to download.
Introduction:
In the ever-evolving business world, there’s been a major shift in how work gets done – the gig economy. It’s altering the very rhythm of work, blending flexibility with new opportunities, and introducing challenges alongside innovation. The gig economy is a game-changer, reshaping how we think about work, business, and organizational structures. In this ebook, explore the inner workings of the gig economy and how it profoundly impacts businesses, workers, and the core of workforce management. We’ll dive deep into understanding the gig economy’s structure, advantages, and challenges and discover strategic approaches for businesses to navigate this new way of working.
The gig economy’s multifaceted nature calls on businesses to reconsider their operational methods, reimagine their managerial strategies, and incorporate cutting-edge technologies to excel in workforce management. As we navigate this transformative era, let’s seize the opportunity to unravel the intricate fabric of the gig economy. We’ll craft a narrative that finds equilibrium between innovation and tradition and adaptability and stability, ensuring businesses thrive in this evolving business landscape.
Understanding the Gig Economy:
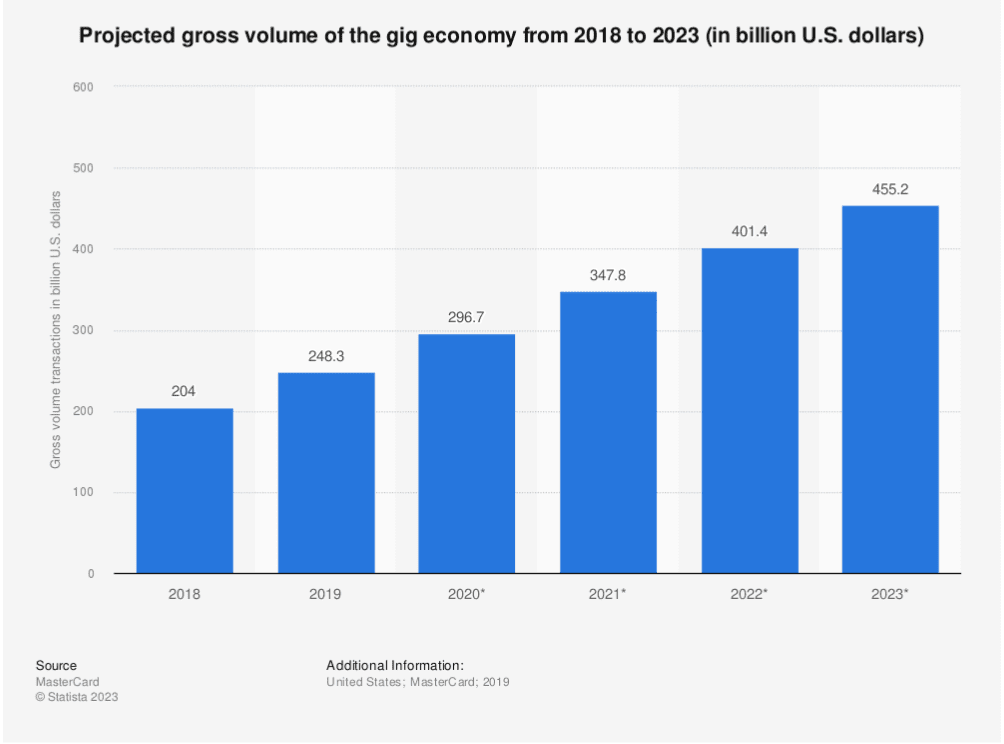
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, the gig economy has emerged as a defining force, transforming how work is organized and performed across various industries. This paradigm shift has given rise to new opportunities and challenges in workforce management. This ebook will delve into the gig economy, its characteristics, and its profound impact on businesses, workers, and platforms. We’ll also explore the advantages and challenges of managing a gig workforce.
The gig economy, often called the “freelance economy” or “on-demand economy,” represents a labor
market characterized by temporary or project-based work arrangements. Unlike traditional employment models, where workers have long-term contracts with one employer, gig workers operate as independent contractors who engage in short-term engagements to perform specific tasks or projects. This flexibility allows individuals to have multiple income streams and work on projects they’re passionate about.
As of 2023, the United States and Canada are firmly on the path to establishing a gig economy, with estimations indicating that up to a third of the working population already engages in gig work. This number is expected to escalate, fueled by the appeal of independent contracting work, often free from the constraints of traditional office environments. A substantial portion of gig workers operate part-time and benefit from the flexibility of working from home, a reality enabled by technological advances.
The gig economy not only expands the pool of applicants available to employers but also allows businesses to tap into talent beyond geographic boundaries. Technological advancements have reached a point where automation and remote work can substitute or complement in-person jobs, revolutionizing the very nature of work itself.
Legal Classification and Historical Significance:

Gig workers’ independent contractor status means they are not entitled to benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, or paid time off. This unique classification has led to legal debates and regulatory discussions surrounding worker rights, job security, and fair compensation. The historical significance of gig work can be traced back to informal jobs and part-time work. Still, the rise of digital platforms has formalized and expanded the gig economy across industries.
The challenge of classifying gig workers within the framework of labor law is a central concern. Historically, the dichotomy between “employee” and “independent contractor” has shaped labor law, but applying these classifications to gig work presents complexities. In the traditional “standard employment relationship” (SER), employees trade autonomy for financial consideration and adhere to their employers’ authority. Gig workers, however, exhibit more independence, having the freedom to choose when they work or if they even work at all.
However, gig workers often grapple with economic dependence and insecurity similar to or exceeding that of traditional employees under the SER. This dichotomy underscores the significance of legally classifying gig workers. Such classification significantly affects entitlements like labor law protections and social benefits. Firms aim to label workers as independent contractors to lower costs, enhance flexibility, and reduce legal risks. Yet, a dilemma arises: firms desire to control work quality while excluding workers from protective employment laws.
Dependent Contractor
In Canada, the concept of a “dependent contractor” emerges, offering a nuanced classification between traditional employees and independent contractors. This intermediary category acknowledges economic dependency and unequal bargaining power. The Dependent Contractor category has historical roots dating back to the 1960s when Professor Harry Arthurs advocated for its recognition. This category extends collective bargaining rights to workers who are notionally “self-employed” but economically dependent.
Over the years, this category found its place in labour relations legislation, allowing workers in various industries, from taxi drivers to dancers, to access collective bargaining—recent legal battles further spotlight gig worker classification.
Ontario Labour Relations Board (OLRB)
The Ontario Labour Relations Board (OLRB) ruled significantly in a landmark decision reverberating through the gig economy landscape. The OLRB determined that platform drivers working for a popular ridesharing company were not independent contractors, as the company had classified them, but “employees” entitled to certain rights, including unionization. This ruling fundamentally altered the labour landscape in Ontario, Canada.
Implications in Ontario, Canada:
This ruling carried profound implications, challenging the conventional gig economy model that relies on classifying workers as independent contractors. By recognizing these drivers as employees, they could form or join labour unions and collectively bargain for better wages, working conditions, and benefits. This decision emphasized the extent of control platform companies exerted over their workers, undermining the argument that gig workers had sufficient independence to warrant contractor status.
United States – California Assembly Bill 5 (AB5):
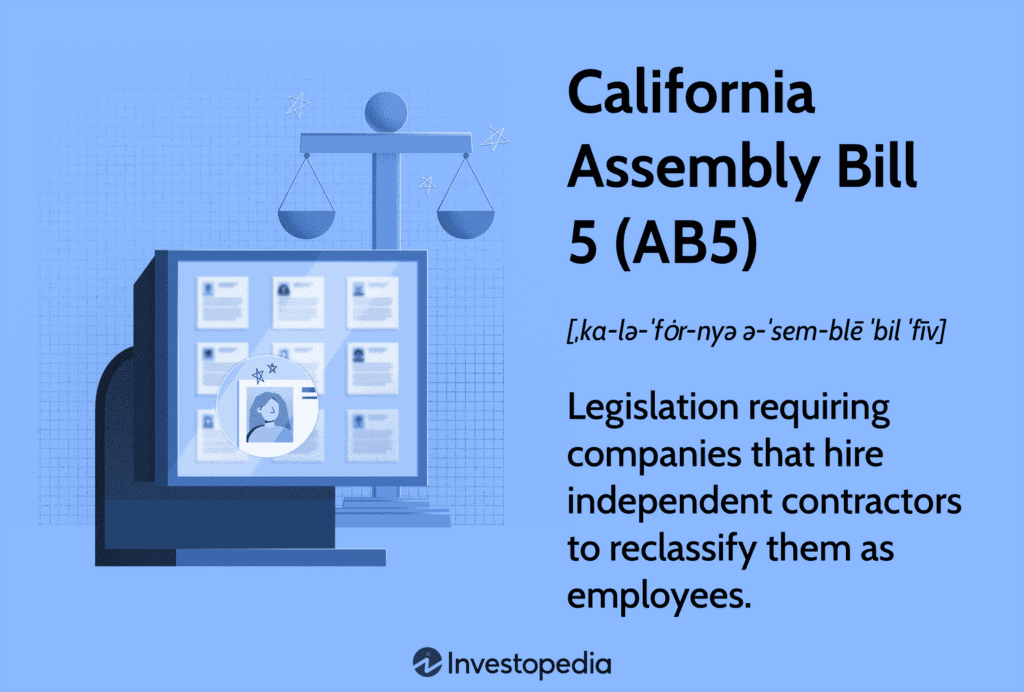
A parallel development in the United States worth noting is the passage of California Assembly Bill 5 (AB5). This legislation, enacted in January 2020, aimed to reclassify many gig workers, particularly those in the ridesharing and food delivery industries, as employees rather than independent contractors. AB5 introduced a stricter test, known as the “ABC test,” to determine a worker’s employment status.
The ABC test typically consists of three criteria, all of which must be met for a worker to be classified as an independent contractor:
- A: The worker is free from the control and direction of the hiring entity in connection with the performance of the work, both under the contract for the performance of the work and in fact. This means the worker has significant independence in carrying out their tasks.
- B: The worker performs work outside the usual course of the hiring entity’s business. In other words, the work being done by the contractor should not be the primary business of the company hiring them. This criterion distinguishes contractors from regular employees who perform core business functions.
- C: The worker is customarily engaged in an independently established trade, occupation, or business that is the exact nature of the work performed. This means the contractor should have their own independent business or professional practice separate from the hiring entity.
Implications in California, United States:
AB5’s impact was significant, requiring gig economy companies to reevaluate their labor practices. The law intended to provide gig workers with minimum wage, overtime, and workers’ compensation benefits. Like the Ontario ruling, AB5 underscored the level of control and dependence many gig workers had on the platforms they worked for. It led to legal battles and debates about the future of work and gig economy labor practices in the United States.
Global Ramifications:
These developments in Canada and the United States had global repercussions, sparking discussions and legal actions in many other countries grappling with the classification of gig workers. The gig economy’s growth had challenged traditional labor norms, and these rulings and legislative changes marked critical attempts to adapt labor laws to the evolving world of work.
Ongoing Debates
This historical and legal backdrop sets the stage for ongoing debates about gig workers’ classification. Courts have challenged mandatory arbitration clauses in gig platforms’ contracts, paving the way for legal proceedings to determine whether gig workers qualify as “employees” under labor standards legislation.
Employee classification principles remain relevant as technology reshapes the gig economy and platforms evolve. Just as traditional taxi and modern gig drivers share parallels, labor boards will likely apply similar reasoning to determine if gig workers qualify as “employees” within labor standards frameworks.
A class-action lawsuit in Ontario exemplifies this issue filed on behalf of Uber drivers. This case highlights the evolving dynamics of platform-based work and the necessity of legally addressing gig worker classification in the context of labor standards legislation.
Industries with Increasing Gig Workers:
The gig economy has permeated various sectors, including transportation, delivery, hospitality, creative services, etc. For instance, ride-hailing platforms like Uber and Lyft and food delivery services like DoorDash and Grubhub are prime examples of how the gig economy has disrupted traditional business models. The gig economy has also made its mark in retail, healthcare, and warehouse labor, as seen in the increasing prevalence of short-term contracts and freelance arrangements.
The gig economy spans virtually every industry, with businesses using gig workers in most sectors, including but not limited to:
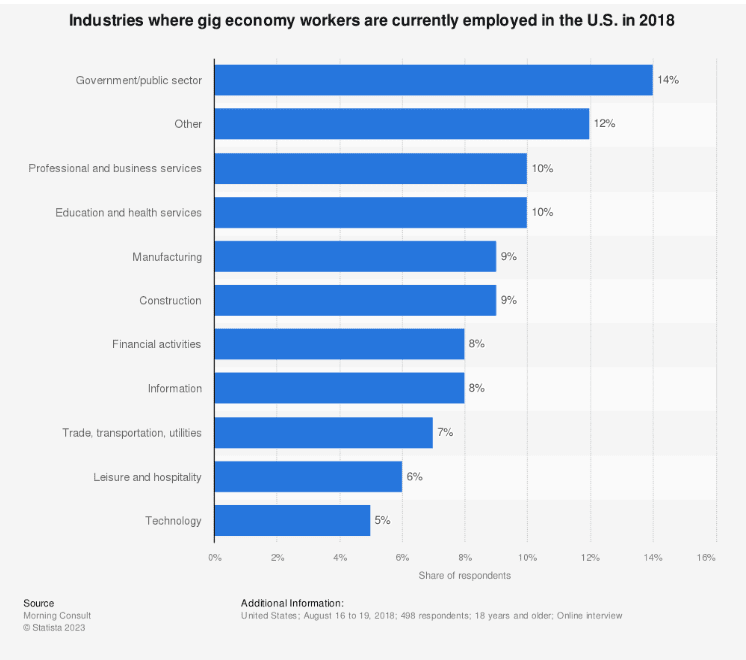
- The public sector including education, health and care services
- Local and central government
- Charities
- Manufacturing
- Construction
- Technology
- Financial services
- Hair and beauty services
- Catering
- Information services
- Business consultancy services
- Transportation
- Leisure
- Hospitality
- SMEs
- Private individuals
The Advantages and Challenges of the Gig Economy:
Benefits for Businesses:
Companies leveraging the gig economy can benefit from cost savings, increased operational flexibility, and access to a diverse talent pool thanks to the gig economy. By hiring gig workers for specific projects, businesses can reduce overhead costs associated with full-time employees. Additionally, tapping into a global talent pool allows organizations to find experts with niche skills, enhancing the quality of their output.

Cost Savings:
One of the most prominent advantages for businesses is the potential for significant cost savings. By leveraging gig workers for specific projects or tasks, companies can avoid the expenses associated with full-time employees, such as benefits, office space, and equipment. This cost-efficient model can significantly impact the bottom line.
Operational Flexibility:
Gig workers bring a level of flexibility to businesses. Organizations can quickly scale up or down based on demand, adapting swiftly to changes in the market. This agility can lead to improved resource allocation and optimized operational efficiency.
Access to a Diverse Talent Pool:
The gig economy transcends geographical boundaries, allowing businesses to tap into a global talent pool. This access to experts with niche skills can enhance the quality of work output, as specialized tasks can be assigned to those with the most relevant expertise.
Benefits for Workers:
Autonomy and Flexibility:

Gig workers relish the autonomy to choose when, where, and how they work. This flexibility allows them to balance their professional and personal commitments, fostering a better work-life balance.
Pursuit of Passion and Interest:
Gig work empowers individuals to choose assignments that align with their skills and interests. This leads to higher job satisfaction, as workers can engage in projects they are passionate about rather than being confined to a single career trajectory.
Skill Diversification and Networking:
Gig workers can explore a diverse range of industries and projects. This experience facilitates the acquisition of a versatile skill set and the expansion of their professional network, both of which contribute to personal and career growth. For example, 30% of younger U.S. adults (ages 18-29) have earned money through gig work at some point.
Challenges for Businesses:
Managing a gig workforce poses challenges related to scheduling and coordination. As gig workers have varying availability and commitments, creating efficient schedules that meet business needs and worker preferences can be complex. Maintaining consistent quality across different gig workers can also be a concern, especially in industries where customer satisfaction is paramount.
Scheduling Complexities:
Gig workers’ varying availability and commitments necessitate sophisticated scheduling solutions to create efficient work schedules that meet business needs and worker preferences.
Quality Consistency:
Maintaining consistent quality across a diverse gig workforce can be challenging, particularly in industries where customer satisfaction is paramount. Ensuring that every gig worker delivers work of the same standard requires robust monitoring and performance evaluation mechanisms.
Challenges for Workers:
Gig workers face uncertainty about income stability, benefits, and job security. The absence of traditional employment benefits and the irregularity of work assignments can lead to financial instability. Additionally, gig workers often need more safety nets than conventional employment provides, such as health insurance and retirement plans.
Income Stability and Benefits:
Earnings can fluctuate due to the nature of project-based work. The absence of traditional employment benefits like health insurance and retirement plans can leave them financially vulnerable. For instance, 24% of gig workers lack health insurance, and 29% earn less than their state’s minimum wage.
Job Security and Safety Nets:
Job security is a concern for gig workers, given the temporary nature of their engagements. The lack of safety nets like health insurance and retirement plans can compound this insecurity, emphasizing the need for comprehensive coverage.
In the dynamic landscape of the gig economy, businesses and workers experience various benefits and challenges. While companies enjoy cost savings, flexibility, and a diverse talent pool, workers relish autonomy, skill diversification, and networking opportunities. Challenges, such as scheduling complexities and income stability, persist for both parties, highlighting the need for innovative solutions and a balanced approach to workforce management.
The Growing Significance of Effective Workforce Management in the Gig Economy
In the evolving landscape of the gig economy, the art of workforce management takes on renewed importance. The dynamic nature of gig work, characterized by flexible schedules, diverse skills, and worker preferences, presents unique challenges that demand innovative solutions. In this section, we delve into the pivotal role of optimizing workforce management in the context of the gig economy, highlighting the complexities of managing gig workers and their distinct challenges compared to traditional employment models.
Unique Scheduling Complexities in the Gig Economy:
The heart of effective workforce management in the gig economy lies in adeptly handling intricate scheduling complexities. Unlike traditional employment models, where employees often adhere to predefined schedules, gig workers operate on a spectrum of flexibility. This variance stems from varying work hours, diverse skill sets, and individual preferences.
Variable Work Hours:
In the gig economy, rigid 9-to-5 schedules give way to the ebb and flow of variable work hours. Gig workers can have unpredictable availability, often juggling multiple assignments or choosing to work during off-peak times. This fluidity challenges businesses aiming to match work demand with available workers. Equipping schedules to meet customer demands while ensuring sufficient coverage requires sophisticated scheduling tools capable of real-time adjustments.

Diverse Skill Sets and Preferences:
Gig workers encompass various skills and preferences, adding another layer of complexity to workforce management. Traditional employment models typically involve specialized roles within an organization. In contrast, the gig economy comprises individuals with varying skill sets, making it crucial for businesses to align specific tasks with the right workers. Moreover, gig workers have preferences regarding the nature of work, location, and timing, necessitating platforms and employers to cater to individual choices.
Challenges of Managing a Gig Workforce:
While the gig economy offers the benefits of flexibility and access to diverse talent, it introduces challenges distinct from conventional employment models.
Scheduling Precision:
The variability in gig workers’ availability requires an advanced scheduling system capable of dynamic adjustments. Traditional scheduling tools might need to catch up in handling real-time modifications to cope with last-minute changes or cancellations, which are prevalent in the gig economy.
Balancing Supply and Demand:
In a gig economy, balancing the supply of available gig workers with the fluctuating demand for their services becomes paramount. Efficiently allocating resources while ensuring customer satisfaction necessitates advanced scheduling solutions that can adapt swiftly to changes in demand patterns.
Maintaining Consistent Quality:
The diversity of gig workers’ skill sets challenges maintaining consistent quality across assignments. Unlike traditional employees who often undergo standardized training and adhere to company guidelines, gig workers may have varying levels of expertise. Ensuring uniform quality requires streamlined methods for monitoring performance and providing feedback.
Fairness and Equity:
The gig economy’s model of work engagement introduces fairness concerns regarding the distribution of assignments among gig workers. Ensuring equitable opportunities for all workers while avoiding the concentration of work on a few individuals demands thoughtful workforce management strategies.
The Role of Technology in Addressing Challenges:
Advanced technology, such as workforce management software solutions like Celayix, is pivotal in tackling the unique challenges of managing a gig workforce.
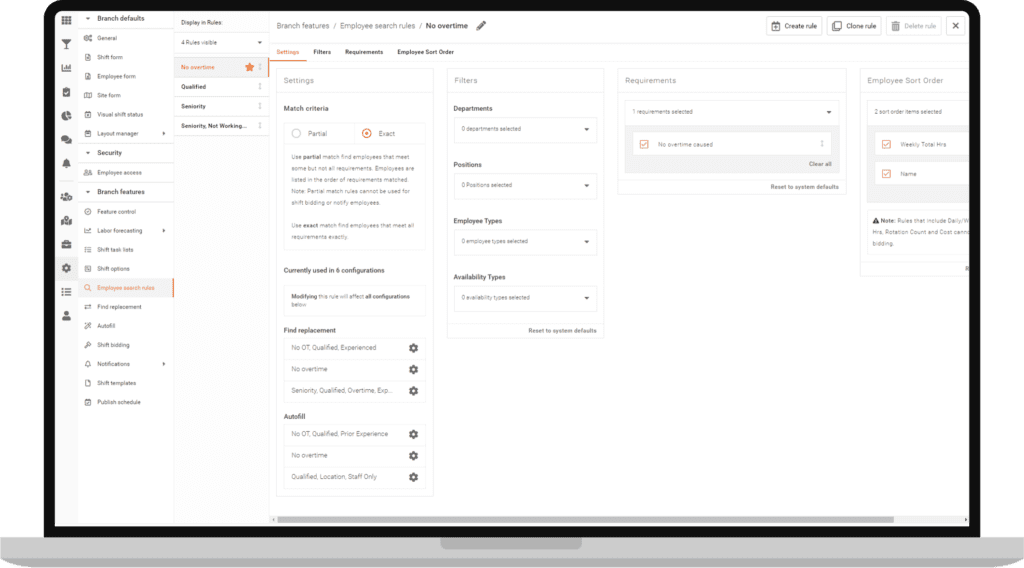
Real-time Adaptability:
Sophisticated scheduling tools enable real-time adjustments, ensuring that businesses can swiftly respond to changes in worker availability and fluctuating demand.
Skill-Based Matching:
Technology facilitates the pairing of tasks with gig workers possessing the relevant skills, enhancing efficiency and quality of service.
Worker Autonomy:
Empowering gig workers to set their availability and preferences through technology fosters a work-life balance and improves engagement and job satisfaction.
Benefits of streamlined scheduling solutions:
Where flexibility and adaptability reign supreme, the intricacies of workforce management and scheduling can be daunting, and the complexities arising from variable work hours, diverse skill sets, and unique worker preferences necessitate innovative solutions that can streamline operations while enhancing worker engagement. Enter advanced scheduling solutions like Celayix, equipped with cutting-edge features driven by AI and machine learning that are tailor-made to navigate the challenges of the modern gig economy.
Embracing Operational Efficiency:
The gig economy thrives on its ability to accommodate flexible schedules, making traditional scheduling methods seem inadequate. Advanced scheduling solutions like Celayix are designed to revolutionize how businesses approach workforce management in this new era. By harnessing the power of AI and machine learning, these solutions analyze historical data and patterns to predict peak demand periods, enabling businesses to allocate resources strategically. This predictive approach ensures that the right workers are available at the right time, enhancing operational efficiency and optimizing customer service.

Seamless and Swift Assignments:
In the gig economy, where gig workers may be engaged in diverse tasks with varying requirements, manual assignment of tasks becomes cumbersome. Celayix’s scheduling solution offers features like shift templates, bulk updates, and assignments that simplify and expedite the process. With the click of a button, managers can create schedules using predefined templates, make bulk updates to multiple assignments, and swiftly assign tasks based on worker availability and skill sets. This saves time and ensures that assignments align with the skills of gig workers, contributing to higher-quality outcomes.
Ensuring Consistency with Find Replacement:
Maintaining consistent quality in a gig economy can be challenging due to the diversity of skills and preferences among workers. Celayix’s “Find Replacement” feature mitigates this challenge by identifying suitable replacements when a gig worker becomes unavailable in real-time. The system analyzes other workers’ skills, availability, and preferences to determine the best fit, ensuring that tasks are seamlessly reassigned without compromising quality or customer satisfaction.
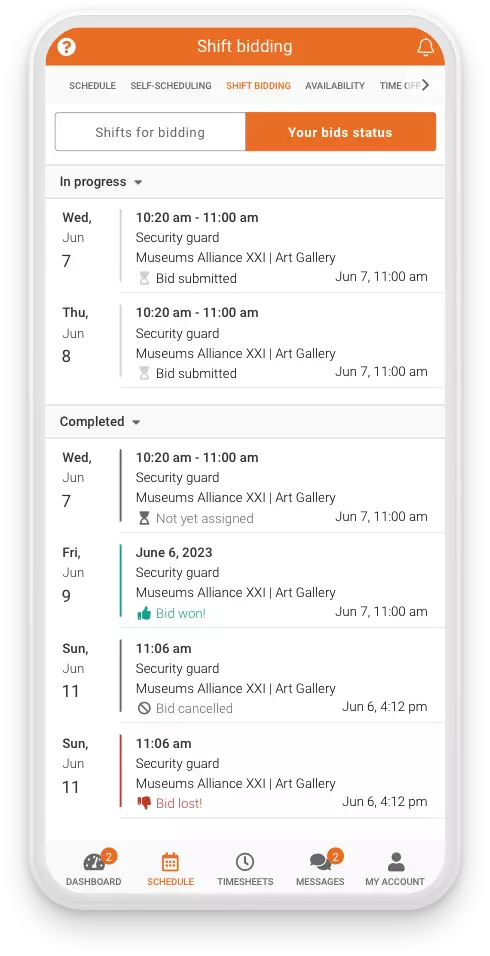
Enhancing Worker Engagement:
Engaging gig workers meaningfully is crucial for retention and overall workforce satisfaction. Celayix’s advanced scheduling solution addresses this need by allowing workers to manage their availability and preferences. Autofill and rotation scheduling features empower workers to express their preferences, enabling them to balance their work commitments with personal life effectively. This level of worker autonomy leads to improved job satisfaction and enhanced engagement, driving productivity and reducing turnover.
Furthermore, Celayix bridges the gap between worker autonomy and managerial control by incorporating features such as shift bidding. Shift bidding allows gig workers to express interest in available shifts, allowing them to choose their preferred work times. This autonomy enhances worker engagement and satisfaction, aligning with the gig economy’s core principles. However, the system maintains a balance by providing schedulers the authority to review bids and make informed decisions. This ensures that the final schedule aligns with business objectives while empowering workers to take ownership of their schedules.
Celayix’s forward-thinking approach transcends traditional scheduling paradigms. Through self-scheduling, Celayix empowers employees to choose their shifts, cultivating a sense of ownership over their work hours. This harmonious blend of individual autonomy and managerial control epitomizes the very essence of the gig economy. By incorporating self-scheduling principles into its arsenal, Celayix aligns with modern workforce values, enhancing worker engagement and productivity.
Embracing the Future with Celayix:
The significance of advanced scheduling solutions like Celayix cannot be overstated in a gig economy that thrives on adaptability and agility. With AI and machine learning capabilities, predictive analytics, and features such as shift templates, bulk assignment, and replacement identification, Celayix empowers businesses to not only meet the unique challenges of the gig economy but also to excel within it. By optimizing scheduling and fostering worker engagement, Celayix paves the way for businesses to navigate the complexities of the gig economy seamlessly.
Key Considerations for Effective Workforce Management in the Gig Economy:
Demand Forecasting and Resource Planning in the Gig Economy
In the dynamic landscape of the gig economy, where adaptability is critical, demand forecasting and resource planning emerge as pivotal factors in ensuring operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. By harnessing the insights from the paper “Designing a Demand Forecasting Service in a Food-delivery Platform,” businesses can better understand the significance of effective demand forecasting and how it intertwines with the gig economy’s unique challenges.
Understanding the Gig Economy’s Demand Forecasting Needs:
The study delves into the demand forecasting service within Wolt, a food delivery platform, showcasing the importance of a user-centric design approach. With Operations Managers (OMs) as the focal point, the study identifies pain points, wishes, and gaps in the demand forecasting process. The study unravels the intricacies of demand forecasting through service design methods and unveils insights that reshape the future of forecasting services. By involving O.M.s in the design process, the study establishes a symbiotic relationship between service providers and users, resulting in more robust and tailored solutions.
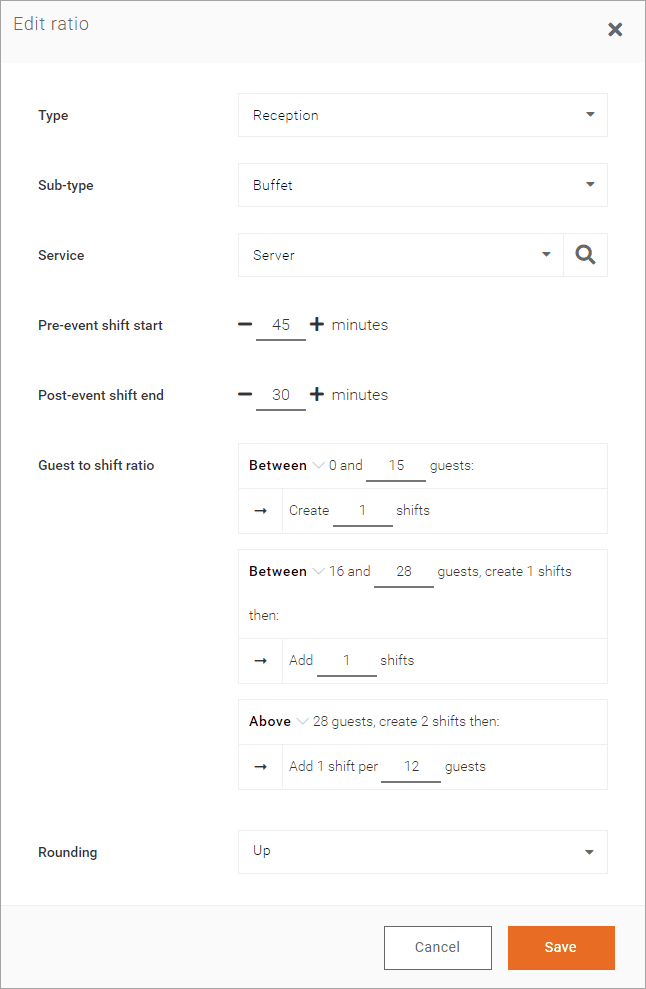
Navigating the Challenges of Demand Forecasting:
One of the challenges highlighted is the diverse user profiles within demand forecasting. The study identifies two distinct profiles: Schedule Dependent O.M.s and Non-Schedule Dependent O.M.s. Each profile approaches demand forecasting differently, impacting their requirements and expectations from the forecasting service. The user journey map elucidates the challenges and opportunities within the current forecasting process. This holistic understanding enables businesses to tailor their solutions to address the unique demands of different user profiles, ensuring accurate forecasts and optimal resource allocation.
Automation and Machine Learning: The Future of Forecasting:
In the gig economy, efficient demand forecasting hinges on automating processes and incorporating external factors. The paper mentioned above emphasizes the role of automated machine learning models in generating accurate and time-efficient forecasts. Businesses can achieve scalability by automating forecasting while factoring in local nuances. Automation enhances accuracy and equips O.M.s with insights into expected growth changes, enabling them to adjust courier supply flexibly.
Centralized Data Gathering and Accessibility:
A crucial element in demand forecasting is collecting and utilizing relevant data. With a centralized data-gathering approach, O.M.s can access historical data and external factors through a centralized service. This ensures consistency and reliability across different markets, enhancing the credibility of forecasts. The paper suggests that a self-service model for calculating demand forecasts can optimize efficiency, reducing time, costs, and manpower required for estimation.

User-Focused Future Forecasting:
The study underscores the need for a forecasting service accommodating flexibility and user-defined factors. By allowing O.M.s to adjust the impact of specific factors on forecasts, businesses can tailor results to local dynamics, boosting reliability. Creating a user-friendly interface and making data easily accessible facilitates efficient decision-making for O.M.s and business stakeholders.
Embracing a Holistic Approach:
The future of demand forecasting in the gig economy lies in comprehensive solutions that encompass both demand and supply aspects. By expanding forecasting efforts to include courier supply, businesses can proactively respond to real-time changes. With a centralized, automated forecasting service, it’s easier to standardize forecasting practices across countries. Such an approach facilitates knowledge sharing, ensuring consistent and efficient demand forecasting across the organization.
Dynamic Scheduling and Shift Flexibility in the Gig Economy
Managing dynamic gig worker schedules is a fundamental challenge that requires a sophisticated approach. Drawing insights from the paper “Flexibility in the Gig Economy: managing time on three online piecework platforms,” this section delves into the intricacies of dynamic scheduling, highlighting the significance of real-time adaptability and worker autonomy.

Adapting Schedules in Real-Time: The Power of Agility:
Gig workers in the digital era are no longer confined by the rigid constraints of traditional working hours. The “tyranny of the clock” concept is replaced by an environment where workers have formal freedom in scheduling their tasks. However, it also uncovers that structural pressures often temper this temporal flexibility. The capacity to adapt schedules in real-time emerges as a pivotal factor in navigating these constraints effectively. A scheduling system that can handle last-minute changes and cancellations becomes crucial, allowing businesses to respond swiftly to emerging demands and unforeseen challenges.
Enabling Gig Workers’ Autonomy: The Key to Satisfaction:
While gig workers can determine their schedules, autonomy is subject to a delicate balance between personal preferences and the platform’s requirements. Empowering gig workers to manage their availability improves their work-life balance and job satisfaction. When workers have the authority to set their preferences, they can align their schedules with their personal lives, enhancing their sense of control and fulfillment. This, in turn, translates into higher levels of engagement and dedication to their gig work.
Structural Constraints and the Quest for Balance:

There is a significant interplay between formal freedom and structural constraints. While gig workers may have the legal authority to shape their schedules, external factors often curtail their ability to exercise this freedom fully. In the gig economy, structural pressures significantly influence how working time is scheduled. This insight underscores the complexity of dynamic scheduling, as it necessitates a delicate balance between worker autonomy and the practical requirements of the platform. Businesses must develop scheduling systems that consider formal flexibility and navigate the underlying structural forces that impact gig workers’ scheduling decisions.
Beyond Control: Towards Worker-Centric Flexibility:
The paper challenges the conventional notion of worker-controlled flexibility as the ultimate ideal. It argues that a more comprehensive approach, termed “worker-centric flexible scheduling,” is essential. Rather than fixating solely on who holds ultimate control, businesses should prioritize how well the scheduling arrangement caters to the worker’s needs and goals. In the gig economy, where cultural-cognitive factors can constrain individual autonomy, the focus should shift towards creating schedules that facilitate effective coordination, enhance subjective time experiences, and contribute to overall job satisfaction.
Technology’s Role in Shaping Temporal Demands:
Technology has played a massive role in shaping gig work’s temporal demands. Different gig platforms incorporate distinct institutional rules into their technological architectures, impacting how workers engage with schedules. While technology provides opportunities for worker empowerment, it is not inherently deterministic in its outcomes. Instead, the design choices made by platform creators are influenced by their goals and ideologies. Moreover, gig workers are not passive recipients of technology but often employ their own “bespoke code” to navigate constraints, emphasizing their agency in shaping their working experiences.
Embracing New Structures of Working Life:
In the dynamic gig economy, new structures of working life are emerging to address the challenges of temporal flexibility. Online communities and practices are evolving among gig workers to adapt to the absence of traditional workplace institutions. These new structures, such as online communities and shared practices, fill the void conventional workplace regulations leave. While they offer flexibility, they also introduce complexities, such as competition and stratification. As technology reshapes work dynamics, businesses must balance fostering inclusive and democratic practices while ensuring equitable access to these emerging structures.
Upholding Compliance and Quality in the Gig Workforce
While the gig model offers unprecedented flexibility and agility, it introduces new challenges related to compliance and maintaining service quality. This section delves into the critical aspects of ensuring compliance and quality in the gig workforce.

Compliance in the Gig Economy: Striking a Delicate Balance:
The traditional boundaries between full-time employment and contract work are becoming increasingly blurred in the gig economy. Workers opt for gig arrangements to gain the flexibility to define their schedules, while employers embrace this trend to access specialized skills flexibly. However, amidst this transformative landscape, the challenges of compliance with labor laws and regulations cannot be ignored. Regulatory bodies, including the U.S. Department of Labor and the Internal Revenue Service, vigilantly monitor how organizations classify and engage gig workers.
The Dynamics Driving the Gig Economy:
Flexibility emerges as a primary driving force behind the gig economy. Workers seek the freedom to dictate their work schedules and conditions, relinquishing the stability of traditional employment for autonomy and control. Employers, in turn, tap into this workforce to fulfill immediate business needs without the long-term commitments and costs associated with full-time employees. The 2018 ADP “The Evolution of Work” study highlights the enthusiasm among North American workers for defining their work schedules in a way that aligns with their convenience and effectiveness.
Mitigating Risks through Proper Classification:
A critical compliance risk in the gig economy lies in adequately classifying workers. Misclassifying gig workers as contractors rather than employees can lead to legal consequences, including fines from regulatory authorities. The complexity of this issue is underscored by the IRS test, which requires a detailed understanding of the circumstances to determine worker classification. Failure to adhere to accurate classification guidelines can result in legal repercussions, emphasizing the importance of seeking legal counsel to navigate these intricacies effectively.
Compliance Requires Comprehensive Solutions:
Existing H.R. platforms may need to be equipped to manage the nuances of gig worker engagement and compliance effectively. In many organizations, department managers maintain their lists of contractors, leading to fragmented oversight and potential exposure to compliance risks. Given this landscape, it becomes imperative for companies to adopt comprehensive solutions that can centralize and streamline gig worker management. Such solutions aid credential verification and background checks and ensure adherence to state and federal regulations.
Balancing Autonomy with Legal Frameworks:
Balancing autonomy and compliance is paramount as organizations participate in the gig economy. By sharing their engagement processes with experienced employment attorneys, businesses can evaluate whether their practices align with legal requirements. Establishing clear policies and procedures that govern gig worker engagement, along with mechanisms for ongoing communication, contributes to compliance and risk mitigation. Periodic compliance assessments should be conducted, ensuring that deviations are swiftly addressed.
Beyond Legal Compliance: Ensuring Quality Performance:
While compliance with labor laws and regulations is crucial, maintaining service quality in the gig workforce is equally vital. Tracking gig workers’ performance metrics becomes essential to ensure that service levels are met and opportunities for improvement are identified. As gig workers are an integral part of the business, their performance directly impacts customer satisfaction and the company’s reputation.
Future Trends in the Gig Economy and Workforce Management:
Technological and Regulatory Progression
As the gig economy continues to redefine the world of work, a confluence of technological advancements and regulatory responses shapes the landscape of gig workforce management. In this section, we explore the intersection of technology and worker protection, focusing on the promises of automation, the global pursuit of equitable treatment, and the imperative of adapting to an evolving gig economy.
Automation and AI-Driven Scheduling: A Symphony of Efficiency
The harmony between technology and workforce management resonates through automation and AI-driven scheduling. Traditionally, scheduling gig workers required manual efforts, risking inefficiencies and errors. Automation, infused with A.I. capabilities, orchestrates a symphony of efficiency. Algorithms analyze historical data, workforce preferences, and operational requirements to compose optimized schedules. This ensures regulatory compliance, reduces fatigue-related mistakes, and aligns shifts with workers’ skills and availability. This fusion optimizes operational precision and elevates worker satisfaction through schedules tailored to their preferences.
Integration with Other H.R. Systems: Creating a Unified Workforce Ecosystem
Integrating technology with other H.R. systems plays a pivotal role in the orchestra of gig workforce management. Harmonizing workforce management software with payroll, benefits administration, and performance management tools creates a unified ecosystem. This concordance streamlines data flow, eliminating redundancies and enhancing decision-making through real-time insights. Seamless integration transcends operational efficiencies, empowering managers with a holistic view of workforce performance. The integration-driven synergy ensures transparency, fosters collaboration, and empowers decision-makers to conduct a harmonious symphony of workforce management.
Adapting to Changing Workforce Dynamics: The Art of Evolution
As the gig economy crescendos, businesses must learn the art of adaptation to orchestrate their success. Strategies for harmonious coexistence encompass future work preparedness and nurturing the gig talent vital for sustained melodies of prosperity.
Preparing for the Future of Work: Orchestrating Readiness
The conductor’s baton guides businesses to prepare for the future in the grand orchestra of gig work. This preparation necessitates embracing remote work and hybrid arrangements. Investing in technologies that facilitate seamless remote collaboration and communication is key. Companies must also strike chords of adaptability, equipping employees and gig workers with skills vital for the evolving work landscape. Through strategic changes, businesses can compose a future-ready workforce adept at navigating change’s intricate melodies.
Nurturing Talent in the Gig Economy: Crafting Harmonious Engagements
A harmonious symphony requires not only skilled musicians but also a nurturing conductor. Similarly, attracting and retaining top gig talent hinges on fostering engagement. By integrating employee engagement initiatives into the orchestration, businesses harmonize gig workers’ experiences. Offering continuous learning platforms, networking opportunities, and recognition solos amplifies gig workers’ sense of belonging. Just as each instrument plays a unique role, gig workers must feel valued and empowered, contributing to the crescendo of an engaged and loyal workforce.
Conclusion: Playing the Gig Economy’s Sonata of Progress
The future of managing gig workers is a blend of technology and regulations. Automation and AI-driven scheduling bring efficiency, and integration creates a unified workforce ecosystem. Adapting to change and nurturing gig talent is vital for continued success. We hear echoes of regulatory reforms and worker protections as we conclude this discussion. The recent actions by British Columbia’s Labour Ministry show that harmony in the gig economy goes beyond technology. It highlights a global conversation embracing the evolving nature of work.
As we wrap up our journey through the gig economy, we have gained valuable insights and a toolbox of strategies. Let’s take a moment to reflect on the intricate dance needed to thrive in the gig economy’s rhythm. The gig economy is a testament to the digital age’s transformative power, inviting businesses to blend technological innovation with strategic wisdom. As this discussion ends, it leaves us with much to ponder and a wealth of knowledge. It encourages us to approach the gig economy with strength and foresight.
In this dynamic landscape, the future belongs to those who adapt without compromising integrity, innovate without sacrificing empathy, and navigate change gracefully. As we venture into uncharted territories, let’s carry the wisdom from this discussion as a compass to navigate the gig economy’s ever-changing waters.





