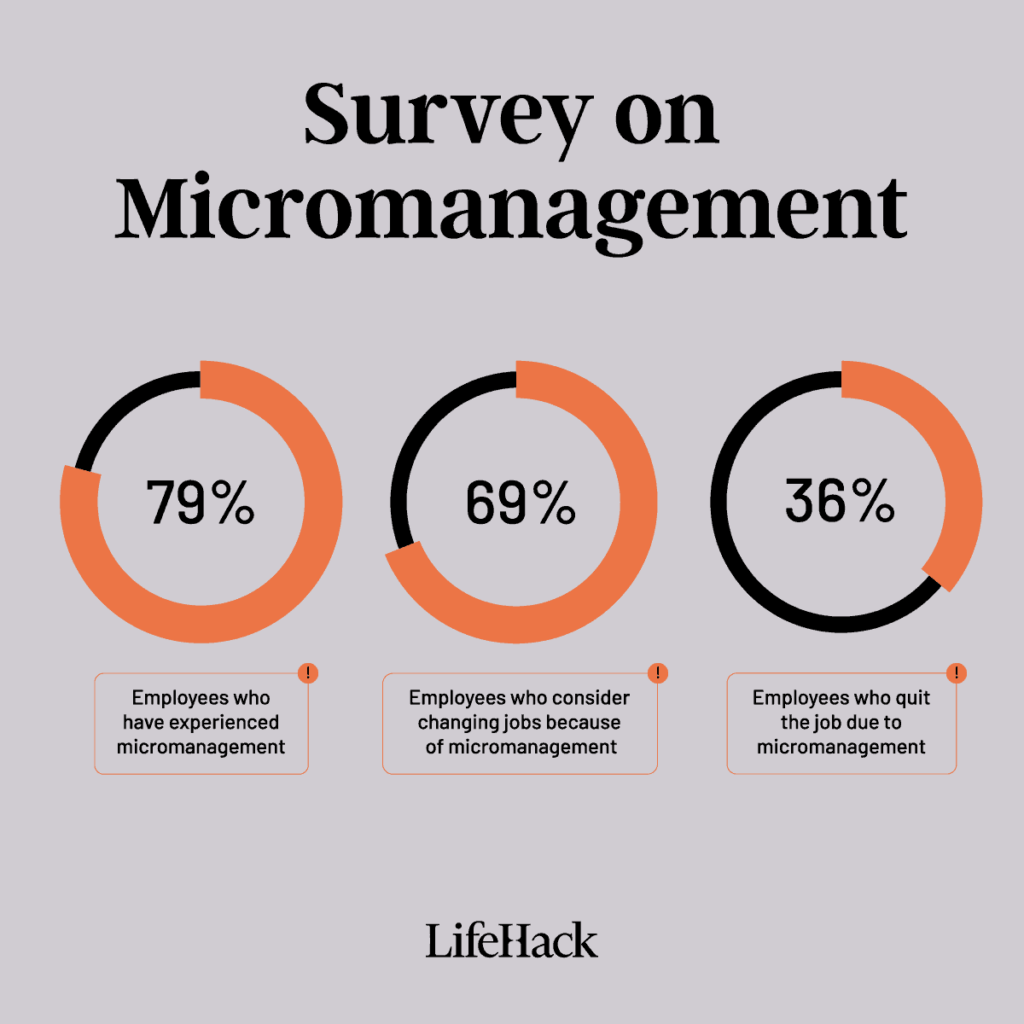
In today’s workplace, micromanagement is a common term. It describes a style where leaders closely watch every part of their employees’ work. While this approach may stem from good intentions, aiming to ensure quality and compliance, it frequently results in unintended negative consequences.
It is important to understand micromanagement, its effects, and how good scheduling can help. This knowledge can create a more productive and happy workforce.
What is Micromanagement?
Micromanagement means paying too much attention to small details of employees’ work. It often includes constant checks, detailed instructions, and not letting others take charge. It’s a management style where leaders feel the need to control or oversee every step of their team’s work, rather than allowing employees the autonomy to manage their responsibilities.
Where and Why is Micromanagement Prevalent?
Micromanagement is prevalent in various industries and organizations, often emerging from a few common scenarios:
- High-Stakes Environments: In industries where precision and adherence to protocols are crucial, such as healthcare or finance, managers may resort to micromanagement to ensure compliance and avoid errors.
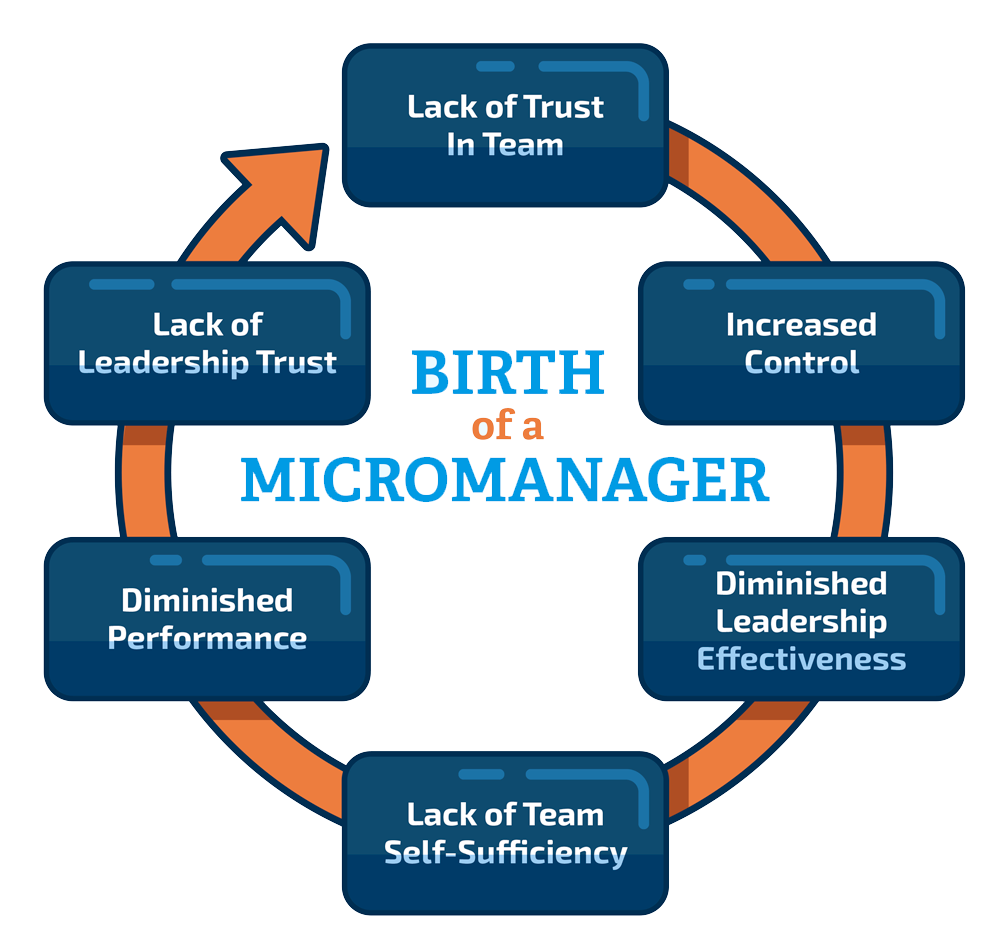
- Lack of Trust: Managers who struggle with trusting their team members’ abilities may find themselves micromanaging to maintain control and reduce perceived risks.
- Inexperience: New managers, eager to prove their competence, might micromanage to demonstrate their involvement and ensure tasks are completed to their standards.
- Pressure to Perform: When facing high-pressure situations or tight deadlines, managers may resort to micromanagement to speed up processes and ensure immediate results.
New managers often face pressure to prove their competence, which can lead them to micromanage out of anxiety and insecurity. They might fear mistakes will damage their reputation or make their direct reports look too competent, causing them to overcontrol. Conversely, hands-off managers, aiming to appear trusting and likable, may go too far and neglect involvement, risking a lack of support for their teams.
The Negative Effects of Micromanagement
While micromanagement might seem like a solution to ensure quality and control, it often backfires, leading to several detrimental effects:
- Reduced Employee Morale: Constant scrutiny and lack of trust can demoralize employees. Feeling undervalued and distrusted, employees may become disengaged and less motivated to perform at their best.
- Decreased Productivity: Micromanagement can lead to inefficiencies, as managers’ focus on minor details slows down decision-making processes. This often results in bottlenecks and a lack of overall productivity.
- Increased Stress Levels: The constant pressure of being monitored can lead to higher stress levels among employees. This stress not only affects their well-being but can also result in higher absenteeism and turnover rates.
- Stifled Creativity: Employees who are micromanaged often find their creative problem-solving abilities stifled. When every step of their work is dictated, they have less opportunity to think outside the box or explore innovative solutions.
The Connection Between Scheduling and Micromanagement
Micromanagement and scheduling are closely linked, as poor scheduling practices can often exacerbate the need for micromanagement. Here’s how:
- Unclear Scheduling: When schedules are poorly defined or constantly changing, managers may feel the need to micromanage to ensure that shifts are covered, and tasks are completed on time.
- Lack of Flexibility: Rigid scheduling that doesn’t account for employees’ preferences or needs can lead to increased dissatisfaction and a perception that managers are not accommodating their team’s needs, prompting further micromanagement.
- Inefficient Shift Management: Poor shift management can create confusion and overlap, leading managers to closely monitor and adjust shifts frequently to prevent issues, rather than trusting employees to manage their schedules independently.
How Effective Scheduling Can Address Micromanagement
Implementing effective scheduling practices can significantly reduce the need for micromanagement and improve overall team dynamics:
Streamline Scheduling Processes:
Advanced scheduling tools, such as Celayix, revolutionize how schedules are created and managed. These tools offer features that simplify scheduling tasks, making them more efficient and less time-consuming.
For instance, Celayix provides real-time access to shift details, which means employees can view their schedules, request time off, and make shift changes without needing constant manager intervention. This increased visibility and control empower employees to manage their own schedules more effectively, reducing the administrative burden on managers.
Furthermore, the tool’s automated scheduling features help in minimizing errors and conflicts, ensuring that shifts are filled accurately and efficiently. By integrating with other HR systems, these tools also help streamline the process of tracking time and attendance, which can be particularly useful for managing large teams or multiple locations.
Empower Employees with Flexibility:
Celayix provides a straightforward and supportive way for employees to manage their own schedules, offering a genuine boost in flexibility. Through its intuitive interface, employees can easily view their current shifts, request changes, and update their availability without needing constant manager intervention.
The platform allows them to submit time-off requests and track their status in real time, receiving automatic notifications about any updates. By enabling employees to handle shift swaps and adjustments directly, Celayix fosters a sense of trust and value, while reducing the need for micromanagement. This approach not only simplifies scheduling but also enhances overall job satisfaction and efficiency.
Leverage Data for Decision-Making:
Modern scheduling systems provide valuable insights into workforce patterns. By using this data to anticipate peak times and plan accordingly, managers can focus on strategic goals rather than micromanaging day-to-day operations.
Focus on Outcomes:
Effective scheduling helps managers shift their focus from overseeing every detail to evaluating outcomes and results. Clear expectations and goals allow employees to work independently, fostering a sense of responsibility and trust.
Build a Culture of Trust:
By implementing transparent scheduling practices, managers can demonstrate trust in their team. This approach not only boosts morale but also encourages employees to take ownership of their work, reducing the need for micromanagement.
Founder Mode: It’s About Clarity, Not Micromanagement
Let’s talk about Founder Mode, the buzzword that’s taking leadership circles by storm. It’s not just for founders—anyone in a leadership position can tap into it. But what exactly is Founder Mode?
Founder Mode: It’s Not Just for Founders Anymore
You might think this term is reserved for scrappy entrepreneurs who live off caffeine and work 80-hour weeks to build their dream company from scratch. But the truth is, anyone can slip into founder mode — even if you’ve never touched a business plan in your life.
So, what exactly is “Founder Mode”? It’s a mindset where leaders dive deep into their business, focusing on the small details that make the big picture work. Paul Graham from Y Combinator kicked off the debate, saying that companies can operate in two distinct ways: Founder Mode and Manager Mode.
While the former is all about staying close to the product and vision, the latter shifts attention to scaling and delegating. Both have their perks, but there’s something magical about staying in “Founder Mode,” even as your company grows.
However, one of the most misunderstood aspects of founder mode is that people assume it means micromanaging every little task. (Cue the collective groan from anyone who’s ever had a micromanaging boss.)
As Graham pointed out, founder mode is about maintaining the spark that made your company special while balancing experienced leadership.
More Clarity on Founder’s Mode
Here’s the kicker: Founder mode does not mean breathing down your team’s necks. Let’s just get that out of the way! Micromanaging is where things go wrong, and our founder and CEO Gurmit couldn’t agree more. He put it this way:
“Yeah, I think a micromanaging approach doesn’t really work. If you’re over their heads and they’re good people, they’re not going to tolerate that… people want to have an impact, and if you’re not giving them the autonomy to make decisions in terms of how that work is going to be done, you’re basically micromanaging them.”
Founder mode is more about clarity, as Brian Chesky of Airbnb pointed out: “There’s a difference between micromanagement and being in the details.” It’s not about constantly checking up on your team; it’s about communicating clear expectations and giving your people the autonomy to hit those goals.
As Rahul Vohra, cofounder and CEO of SuperHuman, said, “If somebody says you’re micromanaging, don’t take that at face value. Your expectations may simply be way higher than what the person can deliver.” It’s often not about mistrust—it’s about ensuring your vision is met, which means keeping a close eye on the big picture while giving your team room to move.
To put it lightly, Founder Mode isn’t “hovering over shoulders” mode. It’s about steering the ship while letting the crew row. Just make sure they’re rowing in the right direction!
In Conclusion
Micromanagement, while often well-intentioned, can hinder productivity, creativity, and employee satisfaction. By recognizing the negative effects and addressing them through effective scheduling practices, organizations can create a more empowered and engaged workforce. Embrace smart scheduling solutions to reduce micromanagement, build trust, and foster a positive work environment where employees thrive and excel.





